NXP JCOP 4 Security Target Lite v3.4 7
6 Extended Components Definition (ASE_ECD)
6.1 Definition of Family ”Audit Data Storage (FAU_SAS)”
This section has been taken over from the certified (BSI-PP-0084-2014) Security IC Platform Protection profile [24].
To define the security functional requirements of the TOE an additional family (FAU_SAS) of the Class FAU (Security Audit) is defined here. This family describes the functional requirements for the storage of audit data. It has a more general approach than FAU_GEN, because it does not necessarily require the data to be generated by the TOE itself and because it does not give specific details of the content of the audit records.
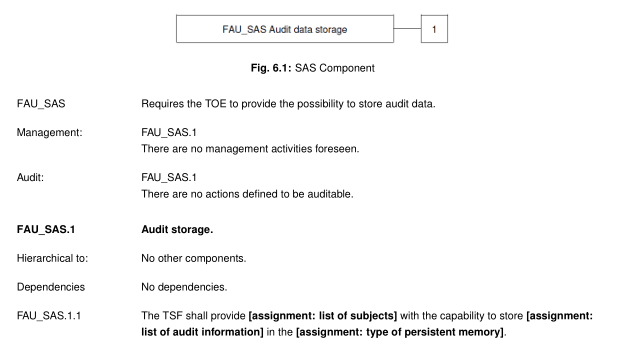
FAU_SAS Audit data storage
Family behavior:
This family defines functional requirements for the storage of audit data.
Component leveling:
6.2 Definition of Family ”TOE emanation (FPT_EMSEC)”
This section has been taken over from the certified (BSI-PP-0055) Protection Profile Machine Readable travel Document with "ICAO Application", Basic Access Control [5].
The sensitive family FPT_EMSEC (TOE Emanation) of the Class FPT (Protection of the TSF) is defined here to describe the IT security functional requirements of the TOE. The TOE shall prevent attacks against the TOE and other secret data where the attack is based on external observable physical phenomena of the TOE. Examples of such attacks are evaluation of TOE’s electromagnetic radiation, simple power analysis (SPA), differential power analysis (DPA), timing attacks, etc. This family describes the functional requirements for the limitation of intelligible emanations which are not directly addressed by any other component of CC part 2 [3].
FPT_EMSEC TOE emanation
Family behavior:
This family defines requirements to mitigate intelligible emanations.
Component leveling:
FPT_EMSEC TOE emanation | 1 | ||
Fig. 6.2: EMSEC ComponentFPT_EMSEC TOE emanation has two constituents:FPT_EMSEC.1.1 Limit of emissions requires to not emit intelligible emissions enabling access to TSF data or user data.FPT_EMSEC.1.2 Interface emanation requires not emit interface emanation enabling access to TSF data or userdata.Management: FPT_EMSEC.1
There are no management activities foreseen.Audit: FPT_EMSEC.1
There are no actions defined to be auditable.
FPT_EMSEC. TOE Emanation.
Hierarchical to: No other components.Dependencies No dependencies.FPT_EMSEC.1.1 The TOE shall not emit [assignment: types of emissions] in excess of [assignment: speci-
fied limits] enabling access to [assignment: list of types of TSF data] and [assignment: list
of types of user data].FPT_EMSEC.1.2 The TSF shall ensure [assignment: type of users] are unable to use the following interface
[assignment:type of connection] to gain access to[assignment: list of types of TSF data]
and[assignment: list of types of user data].
7 Security Requirements (ASE_REQ)
This section defines the security requirements for the TOE.
7.1 Definitions
7.1.1 Groups
The requirements are arranged into groups taken from [13]. Further groups are added to cover additional security functional requirements.
Group | Description |
Core with Logical Channels | The CoreG_LC contains the requirements concerning the runtime environment of the Java Card System implementing logical channels. This includes the fire- wall policy and the requirements related to the Java Card API. Logical channels are a Java Card specification version 2.2 feature. This group is the union of requirements from the Core (CoreG) and the Logical channels (LCG) groups defined in [29] (cf. Java Card System Protection Profile Collection [30]). |
(CoreG_LC) | |
Installation (InstG) | The InstG contains the security requirements concerning the installation of post- issuance applications. It does not address card management issues in the broad sense, but only those security aspects of the installation procedure that are related to applet execution. |
Applet deletion (ADELG) | The ADELG contains the security requirements for erasing installed applets from the card, a feature introduced in Java Card specification version 2.2. |
Remote Method Invocation | The RMIG contains the security requirements for the remote method invocation feature, which provides a new protocol of communication between the terminal and the applets. This was introduced in Java Card specification version 2.2. |
(RMIG) | |
Object deletion (ODELG) | The ODELG contains the security requirements for the object deletion capabil- ity. This provides a safe memory recovering mechanism. This is a Java Card specification version 2.2 feature. |
Secure carrier (CarG) | The CarG group contains minimal requirements for secure downloading of ap- plications on the card. This group contains the security requirements for pre- venting, in those configurations that do not support on-card static or dynamic bytecode verification, the installation of a package that has not been bytecode verified, or that has been modified after bytecode verification. |
External Memory (EMG) | The EMG group contains security requirements for the management of external memory. |
Configuration (ConfG) | This group contains security requirements related to the configuration of the TOE. |
Secure Box (SecBoxG) | This group contains security requirements to separate the native code executed in the Secure Box environment from the rest of the TOE. |
This group contains security requirements concerning the modular design of the TOE. | |
Restricted Mode (RMG) | This group contains security requirements concerning restriction of the TOE functionality in case the Attack Counter expires. |
Further Security Functional | This group contains further security requirements not covered by the PP [13]. |
Requirements | |
Tab. 7.1: Requirement Groups |
7.1.2 Subjects
Subjects are active components of the TOE that (essentially) act on the behalf of users. The users of the TOE include people or institutions (like the applet developer, the card issuer, the verification authority), hardware (like the CAD where the card is inserted or the PCD) and software components (like the application packages installed on the card). Some of the users may just be aliases for other users. For instance, the verification authority in charge of the bytecode verification of the applications may be just an alias for the card issuer. Subjects (prefixed with an "S") are described in the following table:
Subject | Description |
S.ADEL | The applet deletion manager which also acts on behalf of the card issuer. It may be an applet ([39], §11), but its role asks anyway for a specific treatment from the security viewpoint. This subject is unique and is involved in the ADEL security policy. |
S.APPLET | Any applet instance. |
S.CAD | The Card Acceptance Device (CAD) represents the actor that requests services by issuing commands to the card. It also plays the role of the off-card entity that communicates with the S.INSTALLER. |
S.INSTALLER | The installer is the on-card entity which acts on behalf of the card issuer. This subject is involved in the loading of packages and installation of applets. |
S.JCRE | The runtime environment under which Java programs in a smart card are exe- cuted. |
S.JCVM | The bytecode interpreter that enforces the firewall at runtime. |
S.LOCAL | Operand stack of a JCVM frame, or local variable of a JCVM frame containing an object or an array of references. |
S.SD | A GlobalPlatform Security Domain representing on the card a off-card entity. This entity can be the Issuer, an Application Provider, the Controlling Authority or the Verification Authority. |
S.MEMBER | Any object’s field, static field or array position. |
A package is a namespace within the Java programming language that may contain classes and interfaces, and in the context of Java Card technology, it defines either a user library, or one or several applets. | |
S.SBNativeCode | The third party native code executed via the Secure Box mechanism. |
S.Customer | The subject that has the Customer Configuration Token. |
S.NXP | The subject that has the NXP Configuration Token. |
S.ConfigurationMechanism | On card entity which can read and write configuration items. |
Tab. 7.2: Subject Descriptions |
7.1.3 Objects
Objects (prefixed with an "O") are described in the following table:
Objects | Description |
O.APPLET | Any installed applet, its code and data. |
O.CODE_PKG | The code of a package, including all linking information. On the Java Card platform, a package is the installation unit. |
O.JAVAOBJECT | Java class instance or array. It should be noticed that KEYS, PIN, arrays and applet instances are specific objects in the Java programming language. |
O.EXT_MEM_INSTANCE | Any External Memory Instance created from the MemoryAccess Interface of the external package from the Java Card API [38]. |
O.SB_Content | The code and data elements of the native code library residing in the Secure Box. This includes SecureBox support functionality provided by the TOE, like functionality to write into FLASH memory or execute Crypto Library code. |
O.NON_SB_Content | Any code and data elements not assigned to the native code library residing in the Secure Box. |
O.SB_SFR | The pool of Special Function Registers assigned to be accessible by native code residing in the Secure Box. |
O.NON_SB_SFR | All Special Function Registers which are not assigned to the Secure Box. Es- pecially the Segment Tables to configure the MMU. |
O.PUF | The TOE shall provide a PUF functionality that supports sealing/unsealing of user data. Using this functionality, the user data can be sealed within the TOE and can be unsealed by the same TOE that the user data was sealed on. The PUF functionality comprises import/export of data, encryption/decryption of data and calculation of a MAC as a PUF authentication value. |
Contains Applets, Java code, native code, native code of a library or a com- bination of those. The code of O.CODE_MODULEis called via a dedicated interface. The interface can be TOE internal (if the module implements func- tionality of the JavaCard API) or Public (if the Module implements functionality of the JCOPX API or is accessed via APDUs). Each O.CODE_MODULEhas an unique internal AID. | |
Tab. 7.3: Object Groups |
7.1.4 Informations
Information (prefixed with an "I") is described in the following table:
Information | Description |
I.DATA | JCVM Reference Data: objectref addresses of APDU buffer, JCRE-owned in- stances of APDU class and byte array for install method. |
I.MODULE_INVOCATION | Code execution flow when invoking code inside O.CODE_MODULE. |
Tab. 7.4: Information Groups |
7.1.5 Security Attributes
Security attributes linked to the subjects, objects and information are described in the following table:
Security attributes | Description |
Active Applets | The set of the active applets’ AIDs. An active applet is an applet that is selected on at least one of the logical channels. |
Applet Selection Status | ”Selected” or ”Deselected”. |
Applet’s Version Number | The version number of an applet (package) indicated in the export file. |
Attack Counter | The Attack Counter is triggered when a potential attack is detected. When the Attack Counter reaches its limit, the card moves into restricted mode. |
Context | Package AID or ”Java Card RE ”. |
Currently Active Context | Package AID or ”Java Card RE”. |
Dependent Package AID | Allows the retrieval of the Package AID and applet’s version number. |
LC Selection Status | Multiselectable, Non-multiselectable or ”None”. |
LifeTime | |
1Transient objects of type CLEAR_ON_RESET behave like persistent objects in that they can be accessed only when the Currently Active | |
The Owner of an object is either the applet instance that created the object or the package (library) where it has been defined (these latter objects can only be arrays that initialize static fields of the package). The owner of a remote object is the applet instance that created the object. | |
Package AID | The AID of each package indicated in the export file or the internal AID of a Module. |
Registered Applets | The set of AID of the applet instances registered on the card. |
Resident Packages | The set of AIDs of the packages already loaded on the card. |
Selected Applet Context | Package AID or ”None”. |
Sharing | Standards, SIO, Java Card RE Entry Point or global array. |
Static References | Static fields of a package may contain references to objects. The Static Refer- ences attribute records those references. |
Address Space | Accessible memory portion. |
Customer Configuration Token generation key | The customer key to generate tokens for product configuration. |
NXP Configuration Token | The NXP key to generate tokens for product configuration. |
generation key | |
Configuration Token verification key | The keys to verify tokens for product configuration. |
NXP Configuration Access | The NXP Configuration Access can either be enabled or disabled. |
Customer Configuration Access | The Customer Configuration Access can either be enabled or disabled. |
access privilege | For each configuration item the access privilege attribute defines who (Cus- tomer and/or NXP) is allowed to read/write the item. |
Key Set | Key Set for Secure Channel. |
Security Level | Secure Communication Security Level defined in Section 10.6 of [37]. |
Secure Channel Protocol | Secure Channel Protocol version used. |
Session Key | Secure Channel’s session key. |
Sequence Counter | Secure Channel Session’s Sequence Counter. |
Initial Chaining Vector (ICV) | Secure Channel Session’s ICV. |
Card Life Cycle | defined in Section 5.1.1 of [37]. |
Privileges | defined in Section 6.6.1 of [37]. |
Life-cycle Status | defined in Section 5.3.2 of [37]. |
CPU Mode | The execution mode of the CPU. Can be either user mode, system mode or firmware mode. |
MMU Segment Table | Defines the memory areas which can be accessed for read / write operations or code execution if the CPU is in user mode. Further defines which of the Special Function Registers of the hardware can be accessed in user mode. |
Special Function Registers allow to set operation modes of functional blocks of the hardware. | |
Module Presence | Presence of a particular O.CODE_MODULE inside the TOE with the values ”present” or ”not present”. |
Resident Modules | The set of AIDs of the Modules already present in the card. |
Tab. 7.5: Security attribute description | |
7.1.6 Operations
Operations (prefixed with "OP") are described in the following table. Each operation has parameters given be-tween brackets, among which there is the "accessed object", the first one, when applicable. Parameters may be seen as security attributes that are under the control of the subject performing the operation.
Operations | Description |
OP.ARRAY_ACCESS | Read/Write an array component. |
(O.JAVAOBJECT, field) | |
OP.ARRAY_LENGTH | Get length of an array component. |
(O.JAVAOBJECT, field) | |
OP.ARRAY_AASTORE | Store into reference array component. |
(O.JAVAOBJECT, field) | |
Creation of an object (new or makeTransient call). | |
OP.DELETE_APPLET | Delete an installed applet and its objects, either logically or physically. |
(O.APPLET,...) | |
OP.DELETE_PCKG | Delete a package, either logically or physically. |
(O.Code_PKG,...) | |
OP.DELETE_PCKG_APPLET | Delete a package and its installed applets, either logically or physically. |
(O.Code_PKG,...) | |
OP.INSTANCE_FIELD | Read/Write a field of an instance of a class in the Java programminglanguage. |
(O.JAVAOBJECT, field) | |
OP.INVK_VIRTUAL | Invoke a virtual method (either on a class instance or an array object). |
(O.JAVAOBJECT, method, arg1,...) | |
OP.INVK_INTERFACE | Invoke an interface method. |
(O.JAVAOBJECT, method, arg1,...) | |
OP.JAVA(...) | Any access in the sense of [39], §6.2.8. It stands for one of the opera-tions OP.ARRAY_ACCESS, OP.INSTANCE_FIELD, OP.INVK_VIRTUAL,OP.INVK_INTERFACE, OP.THROW, OP.TYPE_ACCESS, OP.ARRAY_LENGTH. |
2For this operation, there is no accessed object. This rule enforces that shareable transient objects are not allowed. For instance, during the creation of an object, the JavaCardClass attribute’s value is chosen by the creator. | |
Transfer a piece of information I from S1 to S2. | |
OP.THROW(O.JAVAOBJECT) | Throwing of an object (athrow, see [39], §6.2.8.7). |
OP.TYPE_ACCESS | Invoke checkcast or instanceof on an object in order to access to classes |
(O.JAVAOBJECT, class) | (standard or shareable interfaces objects). |
OP.CREATE_EXT_MEM_IN- | Creation of an instance supporting the MemoryAccess Interface. |
STANCE | |
OP.READ_EXT_MEM (O.EXT_ | Reading the external memory represented by O.EXT_MEM_INSTANCE. |
MEM_IN STANCE, address) | |
OP.WRITE_EXT_MEM (O.EXT_ | Writing the external memory represented by O.EXT_MEM_INSTANCE. |
MEM_IN STANCE, address) | |
OP.SB_ACCESS | Any read, write or execution access to a memory area. |
OP.SB_ACCESS_SFR | Any read/write access to a Special Function Register. |
OP.INVOKE_MODULE | Invocation of an O.CODE_MODULE. The invocation of the code is trans-parent to the user. In case O.CODE_MODULE has a TOE internal in-terface and is not present in the TOE, a secure state is preserved by throwing an exception or sending an appropriate error status word to the CAD. |
OP.DELETE_MODULE | Deletion of a Module. |
Tab. 7.6: Operation Description
9 Contents
| 1 ST Introduction (ASE_INT) | |||
| 1.2.3 Required non-TOE Hardware/Software/Firmware | |||
2 Conformance Claims (ASE_CCL) | |||
3 Security Aspects | |||
4 Security Problem Definition (ASE_SPD) | |||
6 Extended Components Definition (ASE_ECD) | |||
7 Security Requirements (ASE_REQ) | |||
8 TOE summary specification (ASE_TSS) | |||
13 Legal information | |||