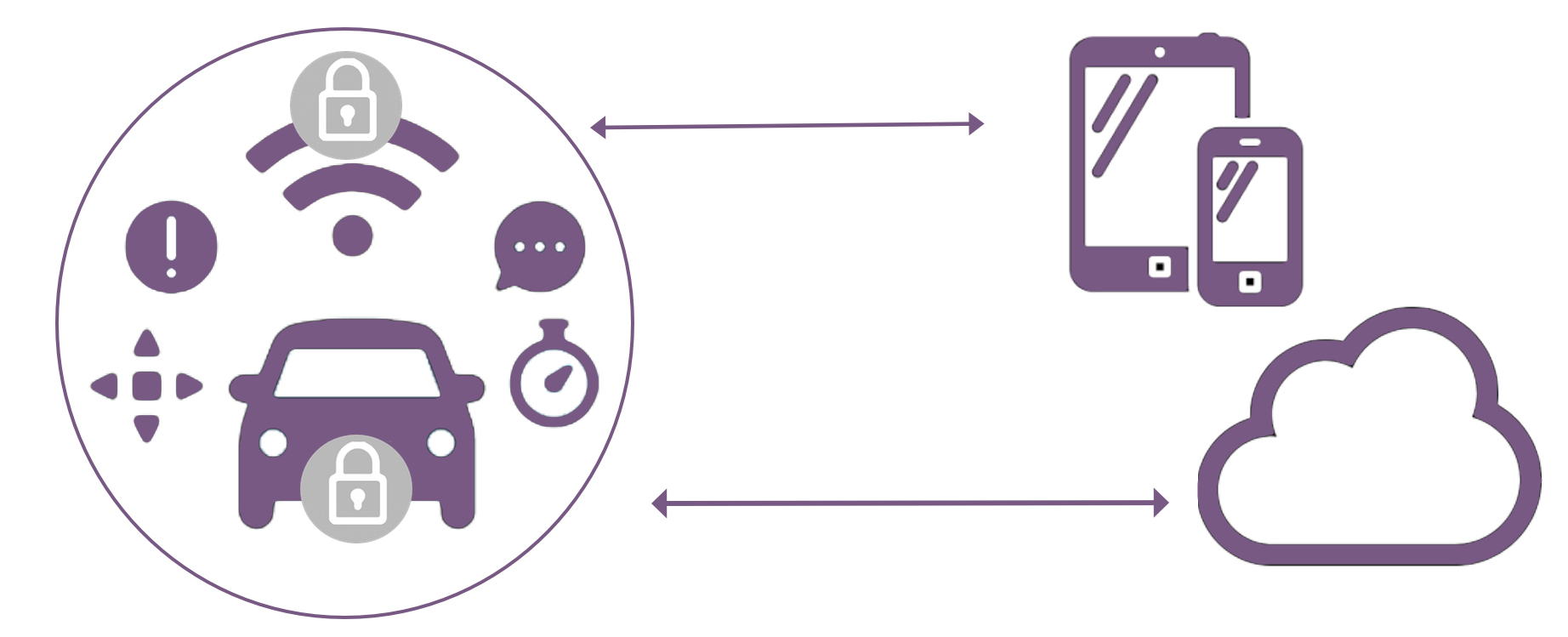
In a world of connected or even autonomously driving cars, privacy, integrity and confidentiality of the data exchanged must be paramount:
Data communication within the vehicle network
Data communication from the vehicle to the cloud or roadside equipment (e.g. geo-location, vehicle specific data, traffic conditions,…)
Data communication from the cloud or roadside equipment to the vehicle (e.g. remote diagnostics, SW updates, …)
Data communication from the user (owner, driver, fleet manager,…) to the vehicle via the mobile device
Java Card based solutions can help to protect and manage the identities of vehicles, their components and their owners / users / drivers from the time of production over the entire lifecycle of the vehicle /device. Java Card can maintain the authenticity and integrity of the exchanged data, as well as the protection against cyber attacks from the Internet or from the infrastructure (e.g. traffic lights, traffic control systems,…). Thanks to the latest Java Card IoT functionality, it can securely handle sensitive data coming from vehicle peripherals and sensors to protect it against tampering and spoofing.
The biggest cyber security challenge for the Automotive industry is that with the connected car; all of a sudden a device gets connected that was not foreseen to be part of the Internet. Yet, the benefits for customers, as well as for producers, are expected to justify the efforts AND the risk:
Consumers demand seamless mobile device integration for ubiquitous reachability
Regulators mandate eCall and collision avoidance capabilities to save lives and make driving more secure
Manufacturers aim to monetize on new opportunities (e.g. predictive maintenance, product
improvements,..)
Four main challenges stem from this hunger for data communication:
Gather the relevant data from the independent sensor endpoints
Process the generated data in “real-time” – locally or in the cloud
Ensure the integrity and authenticity of the generated / collected data
Protect and manage the vehicle /sensor identities over the entire lifecycle of the vehicle (i.e. starting with production)
Java Card can be used to secure the vehicle communication in various ways:
As the security vault for the credentials
As the control gateway managing and controlling all connected endpoints
As the security gateway protecting the in-vehicle communication streams
As the security gateway protecting the communication streams to the cloud
Being already the preferred platform to deploy flexible connectivity Java Cards products are now considered by automotive OEMs to host secure connected car use cases as well.