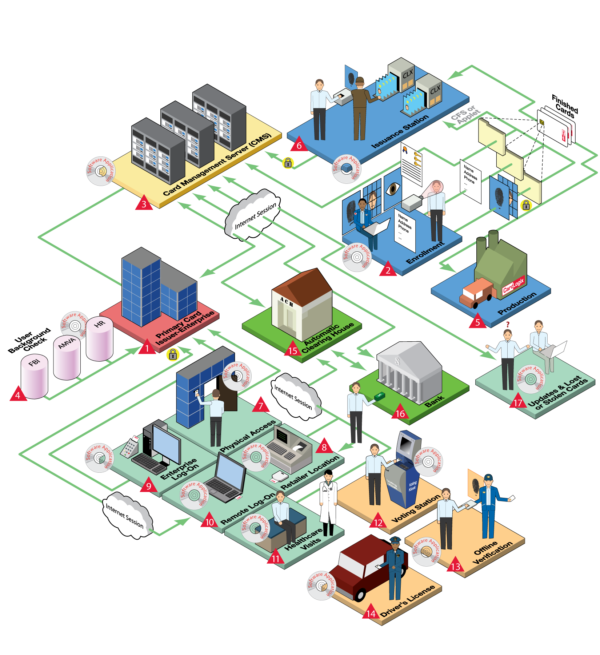
Smart Card System Design Considerations
Is it your job to deploy a smart card system? Are you unsure where to start?
When developing a smart card system, several factors should be considered in advance. Careful planning will help you avoid problems and optimize results in the long run. Consider, for example, the type of information that you will store and how you will protect and share that data. Additionally, you may want to avoid overrunning the system with too many features in the beginning. It could confuse users or create unnecessary difficulties for management. While the inclusion of smart cards requires careful planning and consideration, its advantages are worth the effort. Smart cards and secure elements are the industry standard for identity and device authentication, secure transactions, and the protection of data and assets. The following list of questions and recommendations is intended as a rough guideline to help you get started.
Getting Started: Important Considerations for Smart Card System Design
The First Four
Do you require an original smart card system design? Or, is there an existing application that you can leverage?
Is there a clear business case? Does it include financial and consumer behavior factors?
Will the smart card handle data, value, or both? Adding a value function increases system design security and complexity.
What are the card’s most essential features? With multiple functions, you must prioritize. Start with the most important feature and phase in additional features incrementally.
.
Security
What are your security requirements?
Does all of the data need to be secured (protected)? Or, only some?
Will you include biometrics? Fingerprint, iris, face, signature, and/or other? Do you require 1:1 matching or 1:many?
Will the biometrics be stored in the smart card’s chip for user privacy and distributed user authentication?
Who will have access to this information?
Who will be allowed to change this information?
In what manner will you secure this data? (e.g. encryption, host passwords, card passwords, PINs, etc.)
Should keys/PINs be customer or system activated?
How will you identify the card issuance and versions?
Will the system utilize PKI and Digital Certificates? If so, how will they be managed?
What about security printing options? (e.g. guilloches, microprinting, holograms, hidden images, etc.)
Basic Setup
Will the smart card system be single-application or multi-application?
Are there industry standards (e.g. ISO, EAL, or ETTSI) to conform to for specific encryption or chip requirements?
What information do you want to store in the cards?
How much memory is required for the applications?
If the system is multi-application, how will you separate different types of data?
Will data be obtained from a database or loaded each
time?Will this data concurrently reside on a database?
How many smart cards will be needed?
Have card or infrastructure vendors been identified? What are their lead times?
What are the required readers, handsets, terminals, and software?
Is a Card Management System (CMS) necessary?
How many types of artwork will be included in the issuance?
Who will design the artwork?
What is needed on the card (e.g. signature panels, magnetic stripes, embossing, etc.)?
Deployment Recommendations
Establish clear and achievable program objectives
Analyze the application and IT environment
Make sure the organization has a stake in the project’s success and that management buys into the program
Set a budget
Name a project manager
Assemble a project team and create a team vision
Graphically create a data flow diagram
Assess the card and reader options
Write a detailed specification for the cards and system
Set a realistic schedule with inch stones and milestones
Establish security parameters for people and the system
Build your on-card and host file structures
Phase in each system element and test as you deploy
Reassess your system for security leaks
Deploy the first phase of cards and test the system
Train the key employees responsible for each area
Set up a system user manual
Check the reporting structures
Create contingency plans, should problems arise
Deploy and announce your system
Advertise and market your system